Oxford cloth is a general term for fabrics, which can be nylon, polyester, cotton, acrylic, aramid, etc.
Nylon, also called nylon, is polymerized from caprolactam. Its wear resistance is higher than other natural fibers and chemical fibers. Nylon staple fiber is mainly used for blending with wool or other wool-type chemical fibers. Nylon is added to many textiles to increase their wear resistance. When nylon comes into contact with a flame, it will melt and shrink; it can self-extinguish after leaving the flame and has certain flame retardancy; its residue is a hard light brown and transparent round bead.
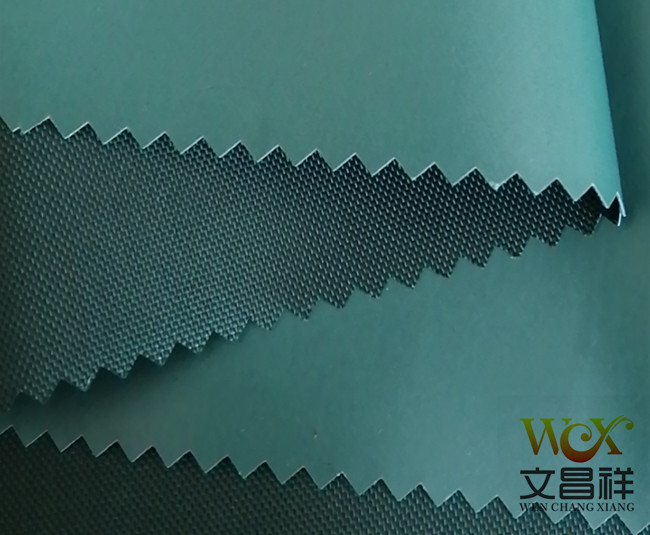

Nylon It has good chemical stability, is resistant to alkali but not acid, and is not resistant to sunlight. The strength will decrease after being exposed to the sun for a long time. Filament yarns are mostly used in the knitting and silk industries; short yarns are mostly blended with wool or wool-type chemical fibers; industrially, they can be used in cords and fishing nets, as well as carpets, ropes, conveyor belts, screens, etc.
Nylon Oxford cloth is light in weight, has good abrasion resistance, high strength chemical resistance and deformation resistance. It gives people a slippery feel and a brighter color, which is similar to polyester Oxford cloth. Compared with nylon Oxford cloth, it is more expensive.
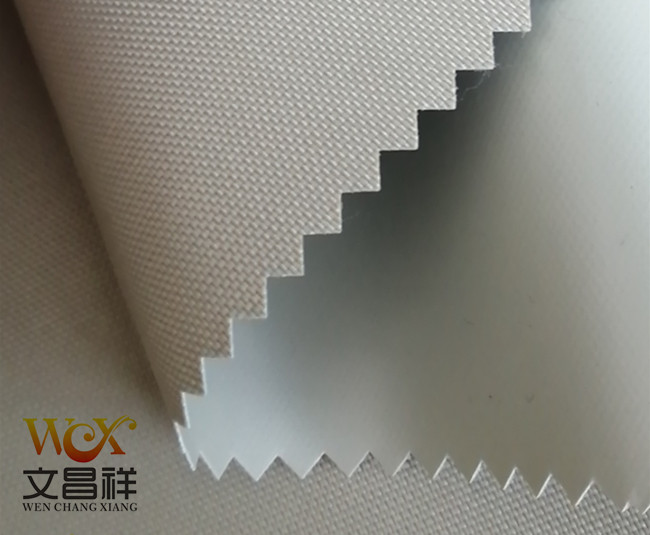
Oxford cloth specifications: 1680D, 1200D, 900D, 600D, 420D, 300D, 210D, 150D, etc.
Oxford cloth functional classification: flame retardant Oxford cloth, waterproof Oxford cloth, PVC Oxford cloth, pu Oxford cloth, camouflage Oxford cloth, Fluorescent Oxford cloth, printed Oxford cloth, composite Oxford cloth, etc.
</p








